-
Url copied to clipboard.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) continues to challenge the corporate agenda due to increasing complexities in a fast-paced, unstable global business environment, brimful of potential yet fraught with trials.
Two risk management styles have emerged from this instability, each with a significant impact on an organisation’s success – proactive and reactive risk management. However, one clearly affords the edge, transforming potential threats into opportunities and delivering on the promise of strategic organisational growth.
Before delving into a comparison, it’s important to understand the basics.
What Is Reactive Risk Management?
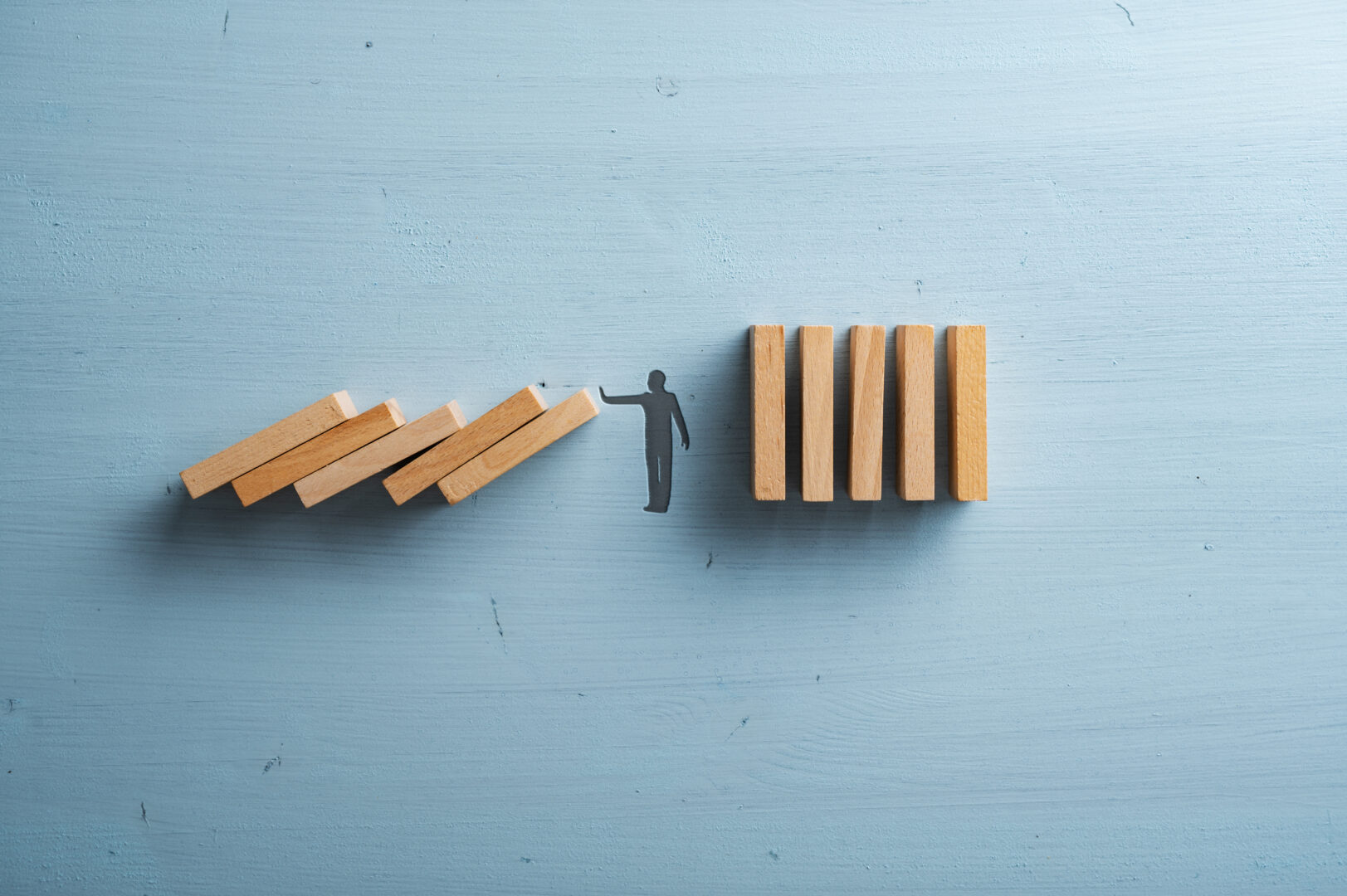
Reactive Risk Management is just as the name suggests. When a risk event occurs, measures are taken to address and mitigate the impact of that event. Reactive risk management can be perceived as firefighting – responding to sudden or systemic disruptions as they occur and attempting to minimise damages thereafter.
In Reactive Risk Management, risk identification is performed based on previous incidents or events that have caused harm, damage, or loss to the business. Risks are mainly identified through Root Cause Analysis based on the historical event data, and steps are then taken to prevent or mitigate the impact of similar events in the future.
While it may appear that reactive risk management comes into play after an incident, it can also serve as a learning tool to retrospectively analyse events and their respective outcomes. It draws on lessons learned from past occurrences to improve reactive/corrective key controls, future prevention and response strategies.
However, one significant shortcoming of this form of management is that it’s often too late to prevent the initial impact of an unexpected risk event. This approach can also be more costly, more resource-intensive, and damaging to the company’s reputation.
So, while organisations should certainly plan for known risks and continuity of operations, they should also consider proactive approaches that identify potential risks in advance, reducing the likelihood of their occurrence. Speaking of which, let’s now explore Proactive Risk Management in more detail.
What Is Proactive Risk Management?
In contrast, Proactive Risk Management, a central tenet of ERM, involves anticipating and managing risks before they materialise. Proactivity enables an organisation to effectively plan and brace itself for potential impact, thereby minimising any harmful consequences. In an ideal Proactive Risk Management environment, strategic planning and foresight convert potential threats into strategic opportunities for growth and improved business resilience.
In this approach, risk identification is not based on past incidents but on future forecasting and predictive modelling. Companies undertake a thorough analysis of their business activities, considering all potential vulnerabilities and threats they may face. This includes everything from economic trends and market shifts to technological advancements or potential supply chain disruptions.
Once potential risks are identified, they are analysed and evaluated to understand their likely impact and probability. The results of this analysis typically inform a business’s strategic planning, ensuring contingency measures are built into operational processes, project plans, and overall strategy.
Following the identification and analysis phase, proactive risk management involves preparing detailed strategies to manage these forecasted risks. This could include allocating resources to mitigate the risk, developing and implementing strong detective and preventative key controls, creating contingency plans, or deciding to accept the risk if it’s deemed a necessary part of doing business.
Regular monitoring and reporting including trend analysis as control steps are also inherent to proactive risk management. The aim is to ensure that the risk management strategies are working as planned and to pick up any changes to the risk environment early.
Overall, proactive risk management not only diminishes the likelihood of negative events occurring but also ensures that organisations are better prepared if they do. It allows for an optimal crisis response, cost, and resource efficiency, and often provides a competitive advantage. It can also contribute significantly to the sustainability and long-term success of an organisation.
Transforming Threats into Opportunities
Business risks are stereotypically viewed as detrimental. However, by adopting a proactive stance, businesses can flip this perception, leveraging risk to their advantage. Here’s how:
Promoting Strategic Decision Making:
Through proactive risk identification and evaluation, ERM enhances strategic decision-making. Leadership can utilise risk intelligence to weigh options, make informed choices and shift business tactics, if need be, thereby converting potential threats into strategic opportunities.
Stimulating Innovation:
A proactive response to risk can often lead to innovation. By encouraging the development of new strategies and solutions to mitigate potential risk, ERM creates an environment conducive to inventive thinking, leading to improved business processes and products.
Seizing Market Opportunities:
Through identification of emerging trends and challenges, ERM can guide an organisation to seize new market opportunities. Timely anticipation and response can result in a first-mover advantage, increased market share and revenue growth.
Building Organisational Resilience:
Proactive risk management practices build organisational resilience and capacity to deal with adverse situations. This resilience not only wards off potential threats but also equips the organisation to seize and maximise opportunities.
Delivering Stakeholder Confidence:
Reactive risk management can undermine stakeholder confidence, whereas proactive risk management can enhance it. Demonstrating to stakeholders that the organisation is capable of anticipating and managing risk effectively often results in increased trust and confidence, leading to better business relationships and opportunities for growth.
The shift from reactive to proactive risk management, with ERM at its core, is integral for businesses operating in an increasingly complex and volatile environment. It allows not only for effective threat mitigation but the transformation of these threats into opportunities for strategic growth and sustainable success.
In an era defined by rapid change, the difference between merely surviving and truly thriving may hinge on the adoption of a well-developed, proactive Enterprise Risk Management approach.
Start Your Enterprise Risk Management Journey with Us
For a more comprehensive, detailed and tailor-made approach to your enterprise risk management, our team of experts can help.
Contact us today to get a deeper insight into this topic from our team of consulting experts.